At HELOC360, we understand that financing a college education can be a daunting task for many families. With rising tuition costs, more parents are exploring alternative funding options beyond traditional student loans.
One such option gaining traction is using a Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) for college tuition. In this post, we’ll explore the pros and cons of this approach and help you determine if it’s the right choice for your family’s educational needs.
How Does a HELOC Work for College Funding?
The Basics of a HELOC
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a line of credit secured by your home that gives you a revolving credit line to use for large expenses. For college funding, it offers a flexible alternative to traditional student loans.
HELOCs function similarly to credit cards, with a credit limit based on your home’s equity. You can typically borrow up to 85% of your home’s value minus your outstanding mortgage balance. For instance, if your home is worth $300,000 and you owe $200,000 on your mortgage, you might qualify for a HELOC of up to $55,000 (85% of $300,000 = $255,000 – $200,000 = $55,000).
Benefits of Using a HELOC for College
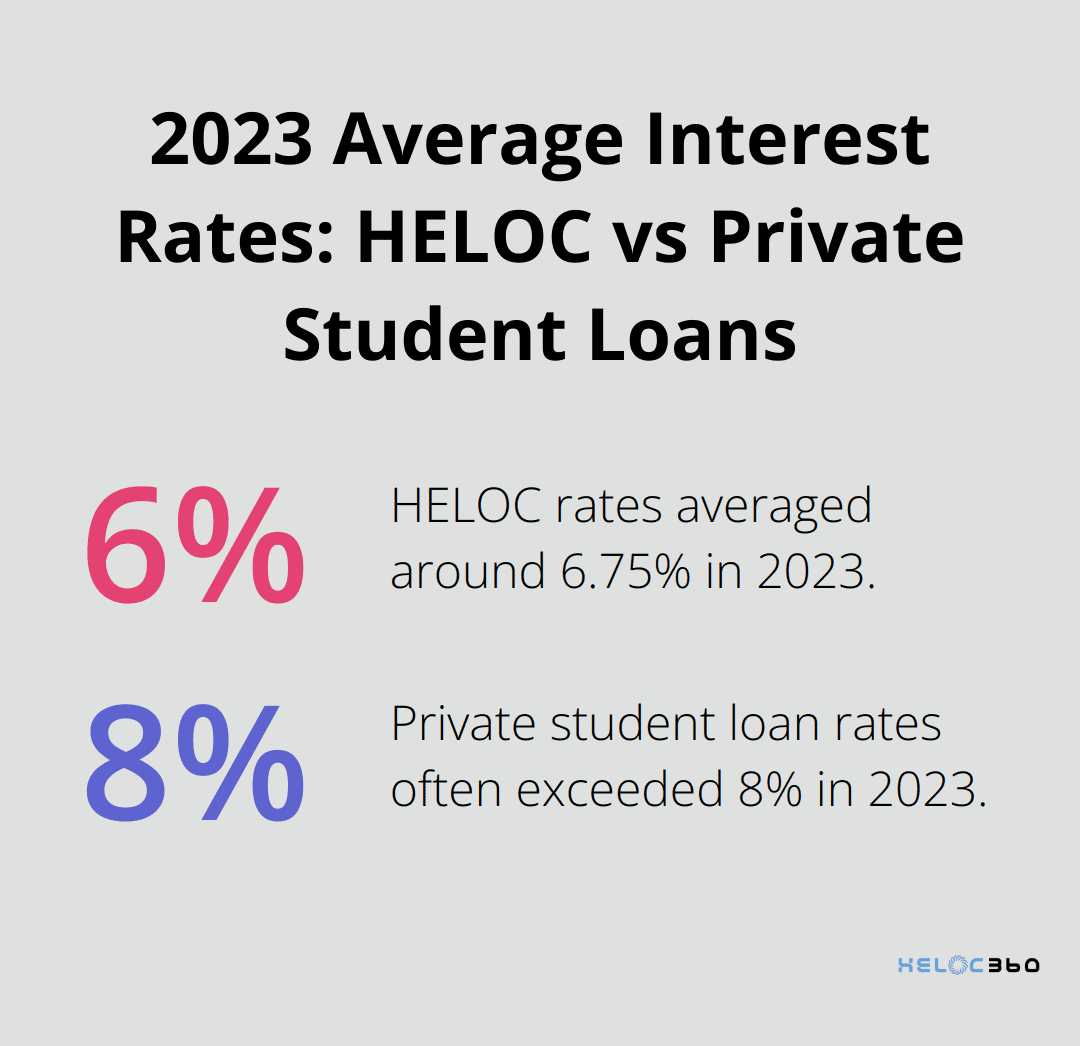
One major advantage of using a HELOC for college expenses is the potential for lower interest rates compared to private student loans. Recent data from Bankrate shows HELOC rates averaged around 6.75% in 2023, while private student loan rates often exceeded 8%.
HELOCs also provide more flexibility than traditional student loans. You can draw funds as needed, which proves particularly useful for covering tuition over multiple years or semesters. This pay-as-you-go approach helps you avoid overborrowing and minimize interest costs.
Risks and Considerations
While HELOCs can offer advantages, they come with significant risks. The most critical risk is that your home serves as collateral. If you fail to repay the HELOC, you could face foreclosure. This contrasts starkly with federal student loans, which offer various protections and forgiveness options.
Another consideration is the variable interest rate typical of HELOCs. While rates might start low, they can increase over time, potentially making your payments less predictable (and more expensive) in the long run.
It’s also worth noting that using a HELOC for college expenses may impact your child’s financial aid eligibility in future years. The funds drawn from a HELOC are considered income on the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA), potentially reducing aid packages.
Exploring Alternatives
We always recommend exploring federal student loan options first, as they often provide more favorable terms and protections. However, if you’ve maxed out federal aid and have significant home equity, a HELOC could bridge the funding gap. Just be sure to carefully weigh the risks and benefits before proceeding.
As we move forward, let’s compare HELOCs to traditional student loans to give you a clearer picture of your options.
HELOCs vs Student Loans: Weighing Your Options
Interest Rates and Repayment Terms
HELOCs and student loans offer different interest rate structures and repayment terms. While specific rates may vary, it’s important to compare the costs, risks, and advantages of each option carefully.
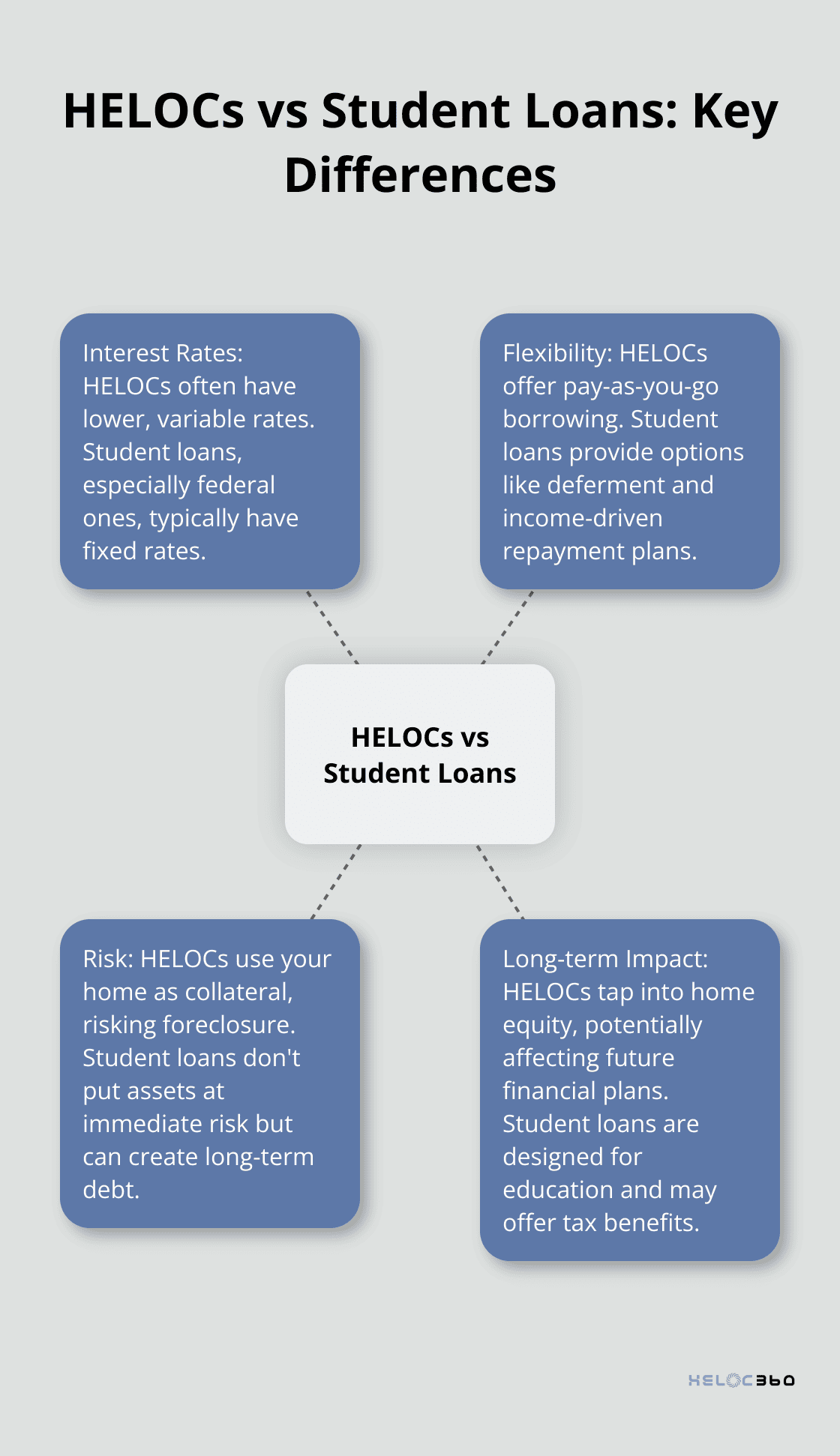
Federal student loans offer fixed interest rates, providing more predictability. This stability can simplify budgeting for many families.
HELOCs excel in flexibility. You can borrow exactly what you need, when you need it (potentially reducing overall interest costs). This pay-as-you-go approach benefits families funding multiple years of education.
Student loans, especially federal ones, offer different types of flexibility. They provide options like deferment and forbearance, which can pause payments during financial hardships. Federal loans also offer forgiveness programs for certain professions, a benefit unavailable with HELOCs.
Credit Score and Future Borrowing Impact
Using a HELOC for college expenses can have a mixed impact on your credit score. It can improve your credit mix (potentially boosting your score), but it also increases your overall debt and reduces available credit (which could negatively affect your score).
Student loans, while also impacting your credit score, are viewed differently by lenders. They’re considered “good debt” because they’re an investment in future earning potential. However, taking on too much student loan debt can still harm your debt-to-income ratio, affecting future borrowing capacity.
It’s important to note that defaulting on a HELOC puts your home at risk of foreclosure, a consequence not faced with student loans. This added risk requires careful consideration when making your decision.
Risk Assessment
HELOCs carry a significant risk: your home serves as collateral. If you fail to repay, you could face foreclosure. This contrasts sharply with federal student loans, which offer various protections and don’t put your assets at immediate risk.
Student loans (especially federal ones) come with built-in safeguards like income-driven repayment plans and potential loan forgiveness. These features can provide a safety net if financial circumstances change after graduation.
Long-Term Financial Impact
Consider how each option affects your long-term financial health. HELOCs tap into your home equity, which could impact your ability to use that equity for other purposes in the future (such as retirement planning or emergencies).
Student loans, while they don’t directly affect your home equity, can create a long-term debt burden. However, they’re specifically designed for education funding and may offer tax benefits that HELOCs don’t provide for educational expenses.
The choice between a HELOC and student loans isn’t always clear-cut. Each option has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on your unique financial situation. As we move forward, let’s explore strategies for using a HELOC wisely if you decide it’s the right option for your college funding needs.
How Much Should You Borrow with a HELOC for College?
Calculate Your Total Education Costs
To start, estimate the full cost of your child’s education. This includes tuition, room and board, books, and other expenses. The College Board reports that for the 2025-2026 academic year, the average annual cost for a four-year public institution is $11,610 for in-state students and $30,780 for out-of-state students. Your actual costs may vary from these averages.
Assess Your Available Home Equity
Determine how much equity you have available. Most lenders allow you to borrow up to 85% of your home’s value minus your outstanding mortgage balance. For example, if your home is worth $400,000 and you owe $250,000 on your mortgage, you might qualify for a HELOC of up to $90,000 (85% of $400,000 = $340,000 – $250,000 = $90,000).
Create a Balanced Funding Plan
Use a HELOC as part of a diversified college funding strategy, not as your sole source of funds. Try to cover no more than 25-30% of total college costs with your HELOC. This approach helps minimize risk and maintains financial flexibility.
For instance, if your total four-year college cost is estimated at $100,000, consider using your HELOC for $25,000 to $30,000 of that amount. Combine this with savings, scholarships, grants, and federal student loans to create a comprehensive funding plan.

Factor in Repayment Capacity
Carefully evaluate your ability to repay the HELOC before borrowing. Consider your current income, job stability, and other financial obligations. A good rule of thumb is to ensure your total monthly debt payments (including your mortgage and potential HELOC payments) don’t exceed 36% of your gross monthly income.
Plan for Interest Rate Fluctuations
HELOCs typically have variable interest rates, which can change over time. When you determine how much to borrow, factor in potential rate increases. Calculate your payments assuming a 2-3% increase in current rates to ensure you can handle higher payments if rates rise.
Final Thoughts
Funding college with a HELOC offers both advantages and risks for families exploring higher education financing options. HELOCs provide competitive interest rates and flexible borrowing, but they also carry significant risks that require careful evaluation. The decision to use a HELOC for college tuition depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals.
We recommend you explore all available options, including federal student loans, scholarships, and grants, before you tap into your home equity. Creating a balanced funding strategy that combines multiple sources will help you mitigate risks and maintain financial flexibility. For some families, a HELOC may bridge the gap between savings and traditional student loans, while for others, the risks may outweigh the benefits.
At HELOC360, we strive to help homeowners make informed decisions about leveraging their home equity. Our platform provides guidance and connects you with lenders that fit your specific needs (including funding education). We encourage you to approach a HELOC with caution and a clear understanding of its implications to make the best choice for your family’s educational and financial future.
Our advise is based on experience in the mortgage industry and we are dedicated to helping you achieve your goal of owning a home. We may receive compensation from partner banks when you view mortgage rates listed on our website.
