- ***PAID ADVERTISEMENT**
- ACHIEVE LOANS – HOME EQUITY EXPERTISE
- FLEXIBLE FINANCING SOLUTIONS
- PERSONALIZED SUPPORT
- RECOMMENDED FICO SCORE: 640+
- COMPETITIVE RATES STREAMLINED APPLICATION PROCESS
Homeowners often face a crucial decision when tapping into their home’s equity: choosing between a home equity line of credit vs cash-out refi. At HELOC360, we understand the importance of making an informed choice.
These two financial tools offer distinct advantages and drawbacks, each suited to different financial situations and goals. In this post, we’ll break down the key differences between HELOCs and cash-out refinances to help you determine which option aligns best with your needs.


- Approval in 5 minutes. Funding in as few as 5 days
- Borrow $20K-$400K
- Consolidate debt or finance home projects
- Fastest way to turn home equity into cash
- 100% online application
Understanding HELOCs: Your Gateway to Home Equity
What is a HELOC?
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) serves as a powerful financial tool for homeowners who want to access their home’s equity. This flexible borrowing option allows you to tap into your home’s value for various purposes. HELOCs offer advantages such as a fixed amount, making impulse spending less likely, fixed monthly payments that make it easier to budget, and lower interest rates than many other loans.
How HELOCs Work
HELOCs function similarly to credit cards, but with your home as collateral. Lenders approve you for a maximum credit limit based on your home’s equity (typically up to 85% of your home’s value minus your mortgage balance). This credit line remains available for a set period, usually 10 years, known as the draw period.
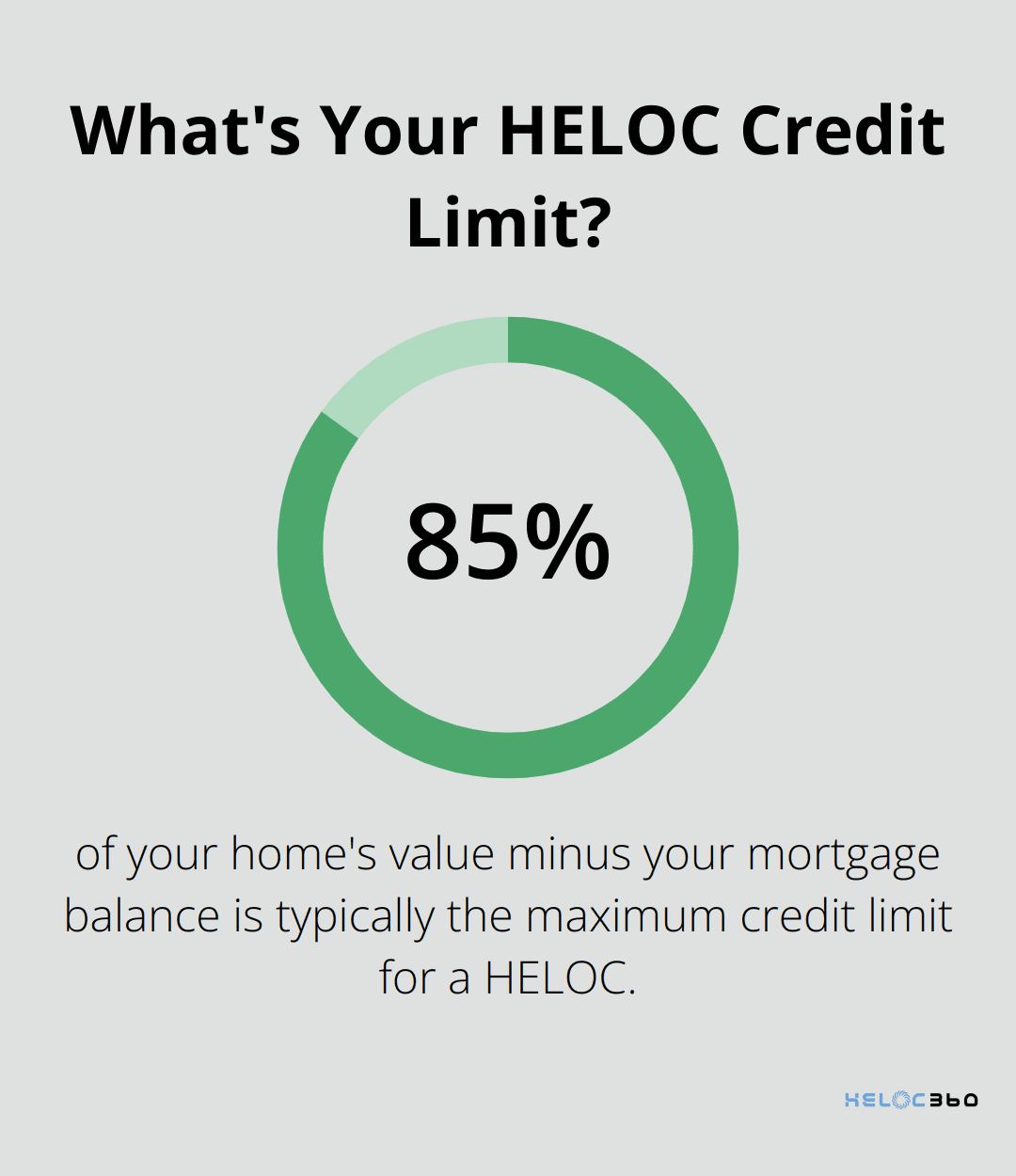
During the draw period, you can borrow as much or as little as you need (up to your credit limit). You only pay interest on the amount you borrow, not the entire credit line. This feature makes HELOCs particularly attractive for ongoing expenses or projects with uncertain costs.
Key HELOC Features
The draw period precedes a repayment period, which typically lasts 10 to 20 years. During this time, you can no longer borrow from the credit line and must repay the principal along with interest.
One important aspect of HELOCs is their variable interest rates. These rates usually tie to the prime rate and can fluctuate over time. While this can lead to lower initial payments, it’s important to prepare for potential rate increases.
Common Uses for HELOCs
HELOCs offer versatility in their applications:
- Home improvements (which can increase property value)
- Debt consolidation (paying off high-interest credit cards or loans at a potentially lower rate)
- Education expenses (funding college tuition, spreading the cost over time)
- Emergency funds (providing peace of mind for unexpected expenses)
- Business funding (for startup costs or managing cash flow, though it’s important to weigh the risks of using your home as collateral)
In 2024, many homeowners used HELOCs for energy-efficient home upgrades. With rising energy costs, investments in solar panels or improved insulation can lead to long-term savings.
The HELOC Advantage
HELOCs provide unique benefits that set them apart from other financing options:
- Flexibility: Borrow only what you need, when you need it
- Potential tax benefits: Interest may be tax-deductible (consult a tax professional)
- Lower initial costs: Often have lower closing costs compared to traditional loans
- Interest-only payments: During the draw period, you may have the option to make interest-only payments
Now that we’ve explored the ins and outs of HELOCs, let’s turn our attention to another popular home equity option: cash-out refinancing. Understanding the differences between these two financial tools will help you make an informed decision about which option best suits your needs.
If you’re considering a HELOC for an investment property, it’s important to research lenders in your state that offer this option. For those new to the home buying process, it’s advisable to start with a comprehensive guide that walks you through each step of purchasing and financing a home.
Cash-Out Refinance: A Different Approach to Home Equity
What is Cash-Out Refinancing?
Cash-out refinancing allows you to use your home as collateral for a new loan, creating a new mortgage for a larger amount than currently owed. This option differs from a traditional refinance, which typically aims to secure a better interest rate or change loan terms without altering the loan amount.
The Mechanics of Cash-Out Refinancing
When you choose a cash-out refinance, you take out a new mortgage for more than you currently owe on your home. The difference between your new loan amount and your existing mortgage balance becomes cash in your pocket. For instance, if your home is worth $300,000 and you owe $200,000 on your current mortgage, you might refinance for $250,000. This would provide you with $50,000 in cash (minus closing costs).
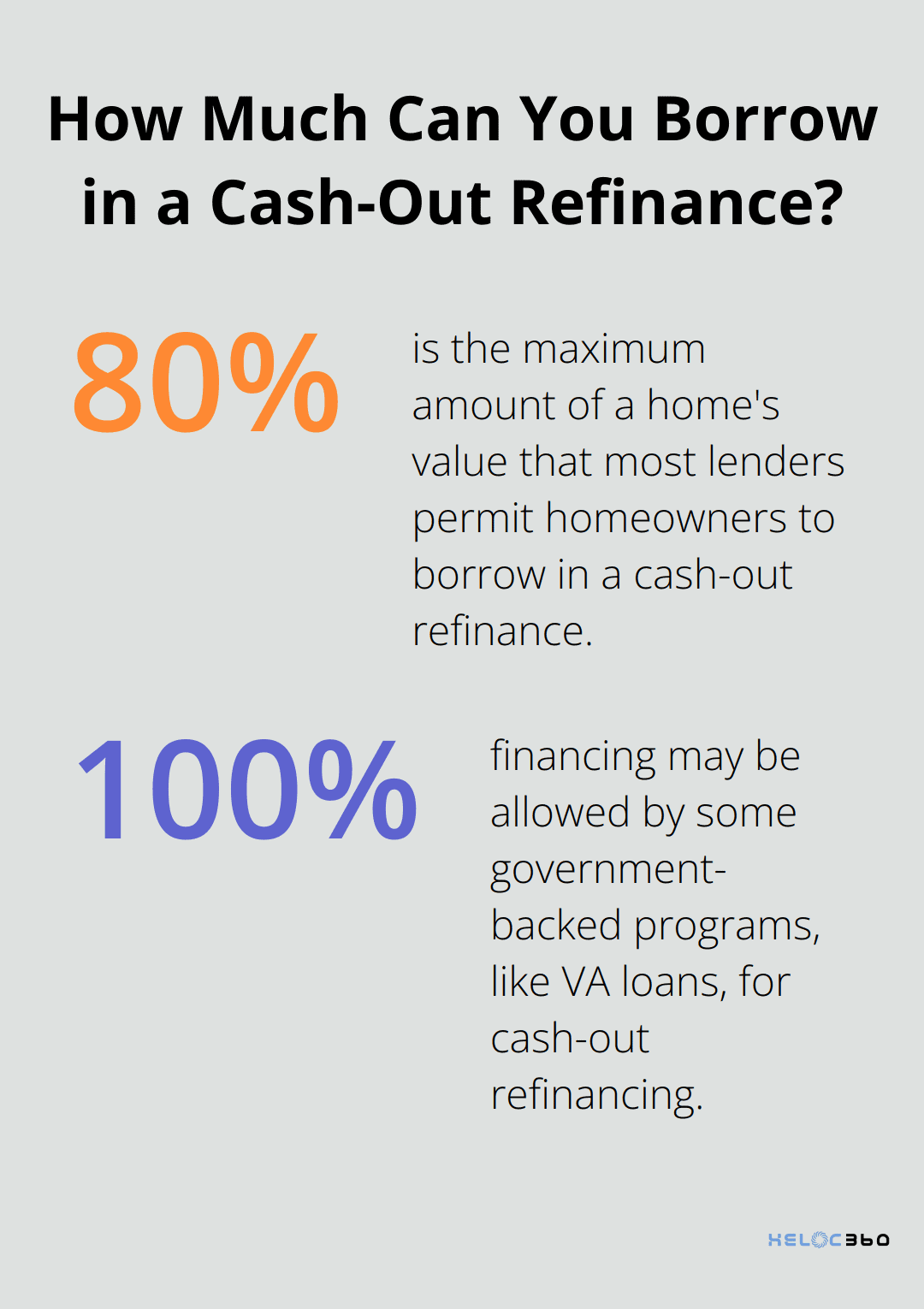
Most lenders permit homeowners to borrow up to 80% of their home’s value. Some government-backed programs, like VA loans, may allow up to 100% financing. It’s important to compare offers from multiple lenders to find the best terms and rates.
Key Distinctions from Traditional Refinancing
A cash-out refinance increases your overall debt, unlike a traditional refinance which simply replaces your existing mortgage with a new one of the same amount. This means a higher loan balance and potentially a longer repayment term. However, it also provides immediate access to a lump sum of cash for various purposes.
Interest rates for cash-out refinances often come with slightly higher rates due to the increased loan amount and perceived risk to the lender. This contrasts with traditional refinancing, which may offer lower rates without changing the loan amount.
Common Uses for Cash-Out Refinancing
Homeowners opt for cash-out refinancing for various reasons:
- Home improvements: Many use the funds to renovate or upgrade their homes (potentially increasing the property’s value).
- Debt consolidation: Paying off high-interest credit card debt or personal loans with the lower-interest mortgage can result in long-term savings.
- Education expenses: Financing college tuition or other educational costs can be more affordable through a cash-out refinance than with student loans.
- Investment opportunities: Some homeowners use the cash to invest in other properties or start a business.
- Major purchases: Funding a new car, wedding, or other significant expense can be more cost-effective through a cash-out refinance than with other forms of financing.
Market Trends and Considerations
The popularity of cash-out refinancing fluctuates with market conditions. In recent years, rising home values have increased the available equity for many homeowners. However, interest rate changes can significantly impact the attractiveness of this option.
Before proceeding with a cash-out refinance, homeowners should carefully consider their financial goals and consult with a financial advisor. While this option can provide substantial benefits when used strategically, it also comes with risks and long-term financial implications.
As we explore the various ways to leverage home equity, it’s essential to understand how cash-out refinancing compares to other options like HELOCs. In the next section, we’ll dive into a detailed comparison of these two popular financing methods to help you determine which might be the right choice for your specific situation.
HELOC vs Cash-Out Refi: Key Differences
Interest Rates and Terms
HELOCs typically come with variable interest rates, while cash-out refinances often offer fixed rates. McBride forecasts that HELOC rates will continue to fall in 2025, sending the average HELOC to 7.25 percent by the end of the year, a low not seen since 2022. This difference can significantly impact your long-term costs.

On a $100,000 loan, you’ll pay about $729 monthly with a HELOC versus $683 with a cash-out refinance over a 30-year term. However, HELOC rates can fluctuate, potentially increasing your payments over time.
Impact on Your Existing Mortgage
A cash-out refinance replaces your current mortgage entirely, potentially changing your loan term and interest rate. It replaces your existing home mortgage with a new, larger loan, and pays you the difference between the new and old mortgage amount at closing. This can benefit you if current rates are lower than your existing mortgage rate. HELOCs, on the other hand, act as a second mortgage, leaving your primary mortgage untouched.
If you’ve recently secured a low fixed rate on your primary mortgage, a HELOC might preserve that rate. Conversely, if your current mortgage has a high rate, a cash-out refinance could potentially lower your overall interest costs.
Flexibility in Borrowing and Repayment
HELOCs offer more flexibility in borrowing. You can draw funds as needed during the draw period (typically 10 years) and only pay interest on what you use. This makes HELOCs ideal for ongoing expenses or projects with uncertain costs.
Cash-out refinances provide a lump sum upfront, which can benefit large, one-time expenses. However, you’ll start paying interest on the full amount immediately.
For repayment, HELOCs often allow interest-only payments during the draw period, followed by principal and interest payments in the repayment period. Cash-out refinances typically require principal and interest payments from the start.
Closing Costs and Fees
Cash-out refinances generally involve higher closing costs, averaging 2-5% of the loan amount. For a $200,000 refinance, you might pay $4,000 to $10,000 in closing costs.
HELOCs usually have lower upfront costs. Some lenders even offer no-closing-cost HELOCs (though these may come with higher interest rates or annual fees). Always compare the total cost over the life of the loan when making your decision.
Tax Implications
Both HELOCs and cash-out refinances may offer tax benefits, but only if you use the funds for home improvements. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated the deduction for interest paid on home equity debt used for other purposes. The interest on a home equity loan is tax-deductible, provided the funds were used to buy or build a home, or make improvements to one, as defined by the IRS.
Consult a tax professional to understand how these options might affect your specific tax situation. The potential tax savings could influence your choice between a HELOC and a cash-out refinance.
Final Thoughts
The choice between a home equity line of credit vs cash-out refi depends on your financial situation and goals. HELOCs provide flexibility with variable rates and as-needed fund access, ideal for ongoing expenses. Cash-out refinances offer lump sums with potentially lower fixed rates, suitable for large, one-time expenses.
Your decision should factor in your current mortgage rate, income stability, and long-term financial plans. HELOCs typically have lower upfront costs but variable rates, while cash-out refinances often come with higher closing costs but offer fixed rates. Your specific financial goals will play a key role in determining the best option for you.
We at HELOC360 understand these complex decisions and want to help you make an informed choice. Our platform simplifies the process of accessing your home equity and connects you with suitable lenders. Visit HELOC360 to explore your options and leverage your home’s value to achieve your financial goals.
Our advise is based on experience in the mortgage industry and we are dedicated to helping you achieve your goal of owning a home. We may receive compensation from partner banks when you view mortgage rates listed on our website.
