Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) offer homeowners a flexible way to tap into their home’s equity. However, understanding the tax implications of HELOCs can be complex and confusing.
At HELOC360, we’ve seen many homeowners struggle with HELOC taxes and their impact on financial planning. This guide will break down the key tax considerations you need to know when using a HELOC, helping you make informed decisions about your home equity borrowing.
What Is a HELOC and How Is It Taxed?
Understanding Home Equity Lines of Credit
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) allows homeowners to borrow against their property’s equity. This financial tool provides flexible access to funds for various purposes, from home improvements to debt consolidation.
The Unique Structure of HELOCs
HELOCs function similarly to credit cards, setting them apart from traditional loans. Lenders approve borrowers for a maximum credit limit based on their home’s equity. During the draw period (typically 10 years), homeowners can access funds as needed.
Evolution of HELOC Tax Treatment
The tax implications of HELOCs have undergone significant changes in recent years. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 significantly altered the rules for deducting home equity loan interest.
Current Tax Deductibility Rules
As of 2025, HELOC interest qualifies for tax deductions only if the funds are used to “buy, build, or substantially improve” the home securing the loan. For example, if you use your HELOC for home renovations, you may deduct the interest. However, interest on funds used for personal expenses or debt consolidation is not tax-deductible.
Limits on Deductions
The IRS imposes limits on HELOC interest deductions. For loans taken out after December 2017, deductions apply to a maximum combined mortgage and HELOC debt of $750,000 ($375,000 if married filing separately).
Practical Considerations for Homeowners
When evaluating a HELOC, it’s important to consider these tax implications. While tax deductions shouldn’t be the sole reason for choosing a HELOC, they can offer significant benefits for qualifying home improvements.
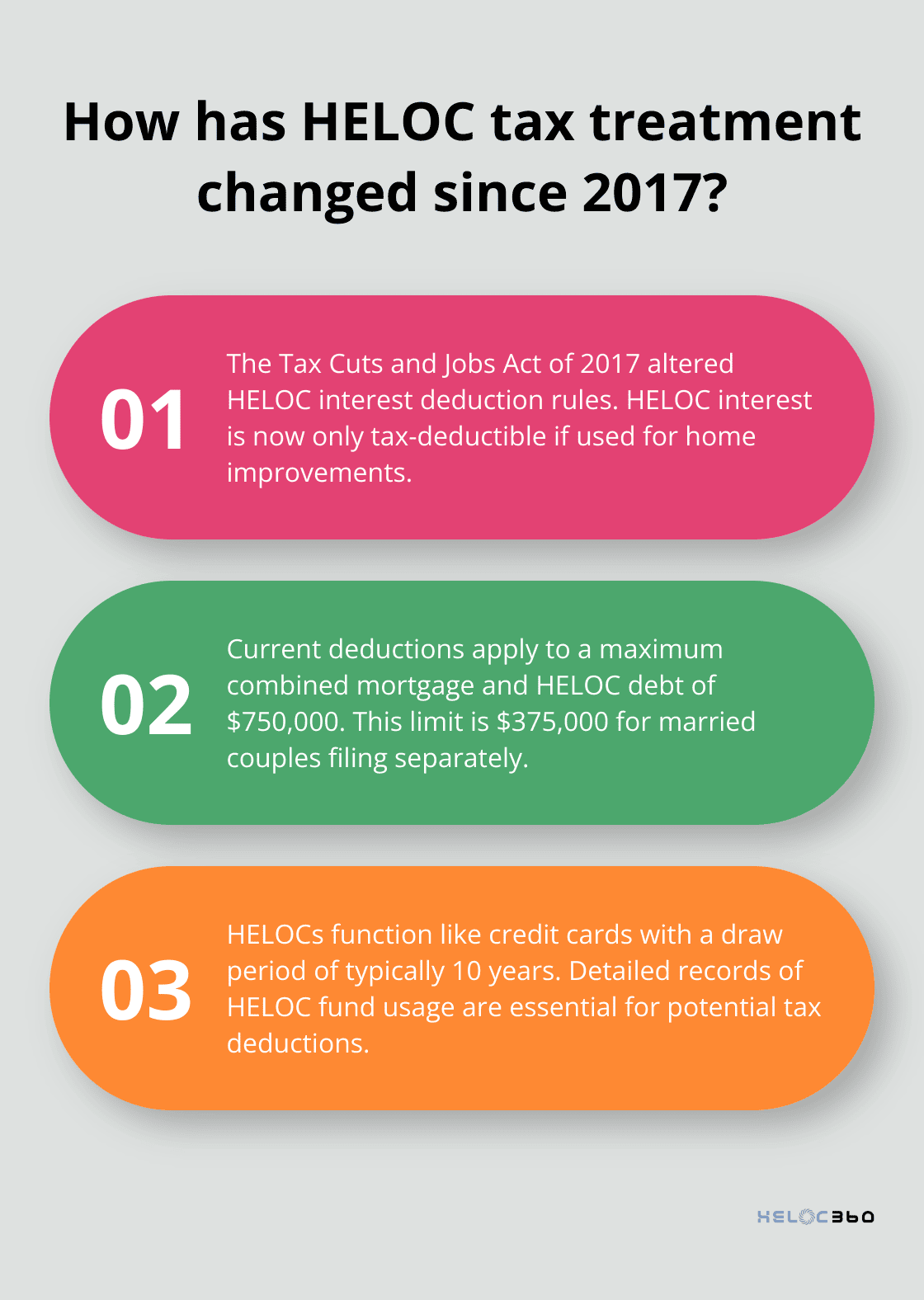
Keeping detailed records of HELOC fund usage is essential (especially for potential tax deductions). This documentation will prove invaluable when filing taxes and can help maximize potential deductions.
The tax landscape for HELOCs continues to evolve, and staying informed about these changes is key to making sound financial decisions. In the next section, we’ll explore the specific scenarios where HELOC interest remains tax-deductible and how to navigate these opportunities effectively.
How to Deduct HELOC Interest: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the New Rules for HELOC Interest Deductions
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 reshaped the landscape for HELOC interest deductions. Under current tax law, you can only deduct interest on HELOC debt if the money you borrow is used to buy, build, or substantially improve the home that secures the loan. This means home renovations typically qualify, while personal expenses or debt consolidation do not.

The IRS has established limits on deductible interest. For loans obtained after December 15, 2017, interest deductions apply to up to $750,000 of combined mortgage debt ($375,000 if married filing separately). This cap includes your primary mortgage and any HELOCs or home equity loans.
Qualifying Uses for Tax-Deductible HELOC Interest
To ensure your HELOC interest remains tax-deductible, focus on home improvement projects that add value to your property. Some examples include:
- Adding a new room or expanding existing spaces
- Upgrading your kitchen or bathrooms
- Replacing your roof or windows
- Installing a new HVAC system
Maintain detailed records of your HELOC fund usage. Save receipts, contracts, and any other documentation related to your home improvement projects. This documentation will prove invaluable if the IRS questions your deductions.
Strategies to Maximize Your HELOC Tax Benefits
To optimize your HELOC’s tax advantages, consider these strategies:
- Plan your home improvements carefully. Prioritize projects that add significant value to your home and align with your long-term goals.
- Time your HELOC usage strategically. If you have multiple projects in mind, space them out to maximize your interest deductions over several tax years.
- Consult with a tax professional. Tax laws can be complex, and a professional can help you navigate the nuances of HELOC interest deductions based on your specific situation.
The Importance of Proper Documentation
Keeping meticulous records is essential when claiming HELOC interest deductions. Create a dedicated file (physical or digital) for all HELOC-related documents, including:
- Loan agreements and statements
- Receipts for materials and labor
- Contracts with contractors or service providers
- Before and after photos of improvement projects
This level of organization will not only simplify your tax preparation but also provide solid evidence should the IRS request additional information.
As we move forward, it’s important to understand that while HELOC interest deductions can offer significant benefits, they shouldn’t be the sole reason for obtaining a HELOC. In the next section, we’ll explore scenarios where HELOC interest isn’t deductible and how this might impact your overall financial strategy.
When Is HELOC Interest Not Tax Deductible?
Non-Qualifying Uses of HELOC Funds
The IRS sets clear guidelines about which HELOC expenses qualify for tax deductions. Using your HELOC for personal expenses or non-home-related costs will disqualify the interest from being tax-deductible. Common non-qualifying uses include:
- Paying off credit card debt
- Financing a vacation
- Purchasing a car
- Covering college tuition
- Investing in stocks or other securities
For example, if you take out a $50,000 HELOC and use $30,000 for a kitchen remodel (qualifying) and $20,000 to pay off credit card debt (non-qualifying), only the interest on the $30,000 would be tax-deductible.
The Alternative Minimum Tax Factor
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) further complicates HELOC interest deductions. If you’re subject to AMT, you might lose the ability to deduct HELOC interest, even if it’s used for qualifying home improvements. The AMT increases the amount of income that is taxed for high earners. The Tax Policy Center reports that about 200,000 taxpayers were affected by AMT in 2022. While this number has decreased since the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, it remains a consideration for high-income earners.
Impact on Your Tax Liability
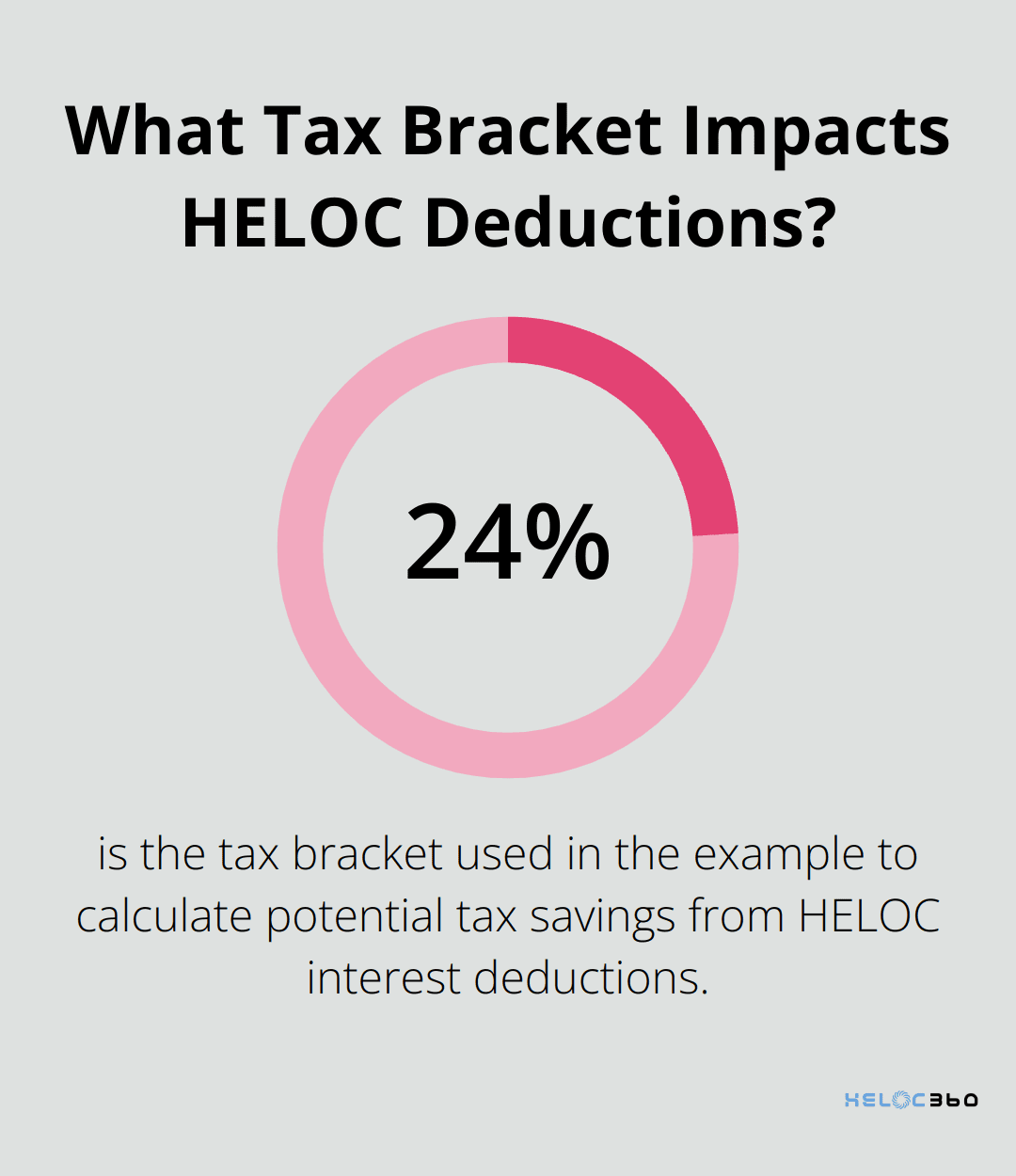
The loss of HELOC interest deductions can significantly affect your overall tax liability. For a $100,000 HELOC at 6% interest, you’d pay $6,000 in interest annually. If this interest isn’t deductible, and you’re in the 24% tax bracket, you’d miss out on $1,440 in tax savings.
Moreover, with the standard deduction for married couples filing jointly set at $30,000 for 2025, many homeowners might find it more beneficial to take the standard deduction rather than itemizing. This shift could negate the tax benefits of HELOC interest deductions altogether.
Consulting with Tax Professionals
The tax implications of HELOCs can catch homeowners off guard. We always recommend consulting with a tax professional before making decisions about HELOC usage. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific financial situation and help you navigate the complex tax landscape surrounding HELOCs.
Record-Keeping for HELOC Expenses
Proper documentation is essential when claiming HELOC interest deductions. Keep meticulous records of all HELOC-related expenses, including receipts, contracts, and statements. This organization will simplify your tax preparation and provide solid evidence should the IRS request additional information.
Final Thoughts
HELOC taxes present a complex landscape for homeowners. The tax implications of HELOCs have changed significantly, making it essential to understand the current rules. HELOC interest is only tax-deductible for qualifying home improvements, with strict limits on eligible debt.

Consulting a tax professional will help you navigate HELOC taxes effectively. They can provide personalized advice based on your financial situation and help you maximize potential tax benefits. This expert guidance ensures compliance with IRS regulations while optimizing your home equity borrowing strategy.
HELOC360 offers solutions to help you make the most of your home’s value. We connect you with lenders that align with your financial goals and provide expert guidance tailored to your needs. Our platform simplifies the process of understanding and managing HELOC taxes, empowering you to make informed decisions about your home equity.
Our advise is based on experience in the mortgage industry and we are dedicated to helping you achieve your goal of owning a home. We may receive compensation from partner banks when you view mortgage rates listed on our website.
