- ***PAID ADVERTISEMENT**
- ACHIEVE LOANS – HOME EQUITY EXPERTISE
- FLEXIBLE FINANCING SOLUTIONS
- PERSONALIZED SUPPORT
- RECOMMENDED FICO SCORE: 640+
- COMPETITIVE RATES STREAMLINED APPLICATION PROCESS
Homeowners often face a crucial decision: HELOC vs refinance. Which option is best for your financial goals?
At HELOC360, we understand the importance of making informed choices about your home equity. This guide will break down the key differences between HELOCs and refinancing, helping you navigate your options with confidence.


- Approval in 5 minutes. Funding in as few as 5 days
- Borrow $20K-$400K
- Consolidate debt or finance home projects
- Fastest way to turn home equity into cash
- 100% online application
What Is a HELOC?
Definition and Key Features
A Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) is a financial tool that allows homeowners to access their property’s value. It functions as a revolving credit line secured by your home’s equity. With a HELOC, you can borrow against your home’s value up to a predetermined limit, as needed.
How HELOCs Operate
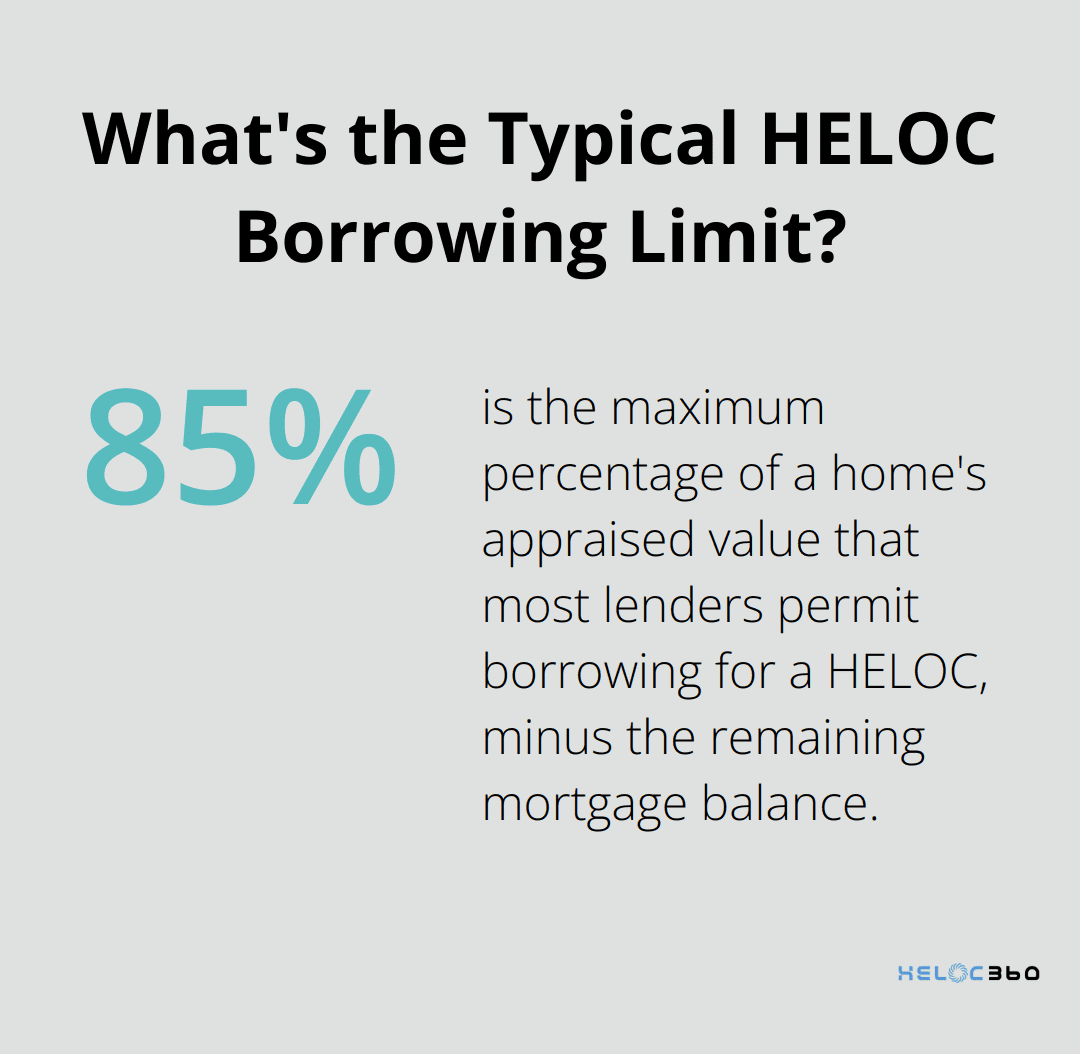
When you open a HELOC, the lender assigns you a credit limit based on your home’s value and your outstanding mortgage balance. Most lenders permit borrowing up to 85% of your home’s appraised value, minus your remaining mortgage balance. For instance, if your home is worth $300,000 and you owe $200,000 on your mortgage, you might qualify for a HELOC of up to $55,000.
HELOCs function in two distinct phases: the draw period and the repayment period. The draw period typically lasts up to 10 years, during which you can borrow funds as needed. You can access these funds by writing checks or using a credit card linked to your HELOC account. During this phase, you’re usually only required to pay interest on what you borrow.
Interest Rates and Repayment Terms
HELOC interest rates are usually variable, which means they can change based on market conditions. As of March 2025, the average HELOC rate is 8.06 percent, according to recent data from Bankrate. However, these rates can vary significantly depending on factors such as your credit score and loan-to-value ratio.
The repayment period begins after the draw period ends and can last up to 20 years. During this time, you can no longer borrow from your HELOC, and you must repay both principal and interest. Your monthly payments may increase substantially during this phase, so it’s important to plan accordingly.
Flexibility and Uses
One of the primary advantages of a HELOC is its versatility. You can use the funds for various purposes, including home improvements, debt consolidation, or even funding a business venture. This flexibility makes HELOCs an attractive option for homeowners who need access to funds over time, rather than a lump sum all at once.
It’s essential to note that a HELOC uses your home as collateral. Failure to make payments could result in the loss of your home through foreclosure. Therefore, it’s vital to borrow responsibly and establish a solid repayment plan.
Many homeowners use HELOCs strategically to achieve their financial goals. Some have funded major home renovations, potentially increasing their property value. Others have used HELOCs to consolidate high-interest debt, which could lead to significant savings in interest payments over time.
As we explore the various options for accessing your home’s equity, it’s important to consider how a HELOC compares to other financial tools, such as refinancing. Let’s examine the refinancing process and its potential benefits in the next section.
Refinancing Your Home Loan: A Comprehensive Guide
What Is Refinancing?
Refinancing replaces your existing home loan with a new one, often with different terms or a new lender. This financial strategy can reshape your homeownership journey and improve your financial situation. However, it requires a thorough understanding of the process and its implications.
Types of Refinancing Options
Several refinancing options exist, each tailored to different financial goals:
- Rate-and-term refinancing: This option aims to secure a lower interest rate or change the loan term. For instance, you might switch from a 30-year mortgage at 4.5% interest to a 15-year loan at 3.5%, potentially saving thousands in interest over the loan’s life.
- Cash-out refinancing: This allows you to borrow more than you owe on your current mortgage and receive the difference in cash. Recent data shows that the refinance share of mortgage applications has reached nearly 44%, hitting its highest point since mid-December. Homeowners often use this option to fund home improvements or consolidate high-interest debt.
Benefits of Refinancing
Refinancing offers several potential advantages:
- Significant savings: A lower interest rate can reduce your monthly payments and save money over time. (On a $300,000 mortgage, lowering your rate by just 1% could save you over $100 per month.)
- Stability: Switching from an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) to a fixed-rate loan provides more stability in your monthly payments. With an ARM, your monthly payments could fluctuate, which can be beneficial if you expect interest rates to rise.
Drawbacks to Consider
While refinancing can offer substantial benefits, it’s not without its challenges:
- Costs: Refinancing typically involves closing costs, ranging from 2% to 6% of your loan amount. The average closing costs are about 3% to 6% of your mortgage’s principal, according to data from the Federal Reserve.
- Extended loan term: If you’ve been paying your current mortgage for several years and refinance to a new 30-year loan, you’re essentially starting over. This could result in paying more interest over the life of the loan, even if your monthly payments are lower.
Making an Informed Decision
Deciding whether to refinance requires careful evaluation of your financial goals, current market conditions, and personal circumstances. It’s essential to compare offers from multiple lenders to ensure you’re getting the best deal. Remember, the lowest interest rate isn’t always the best option if it comes with high fees or unfavorable terms.
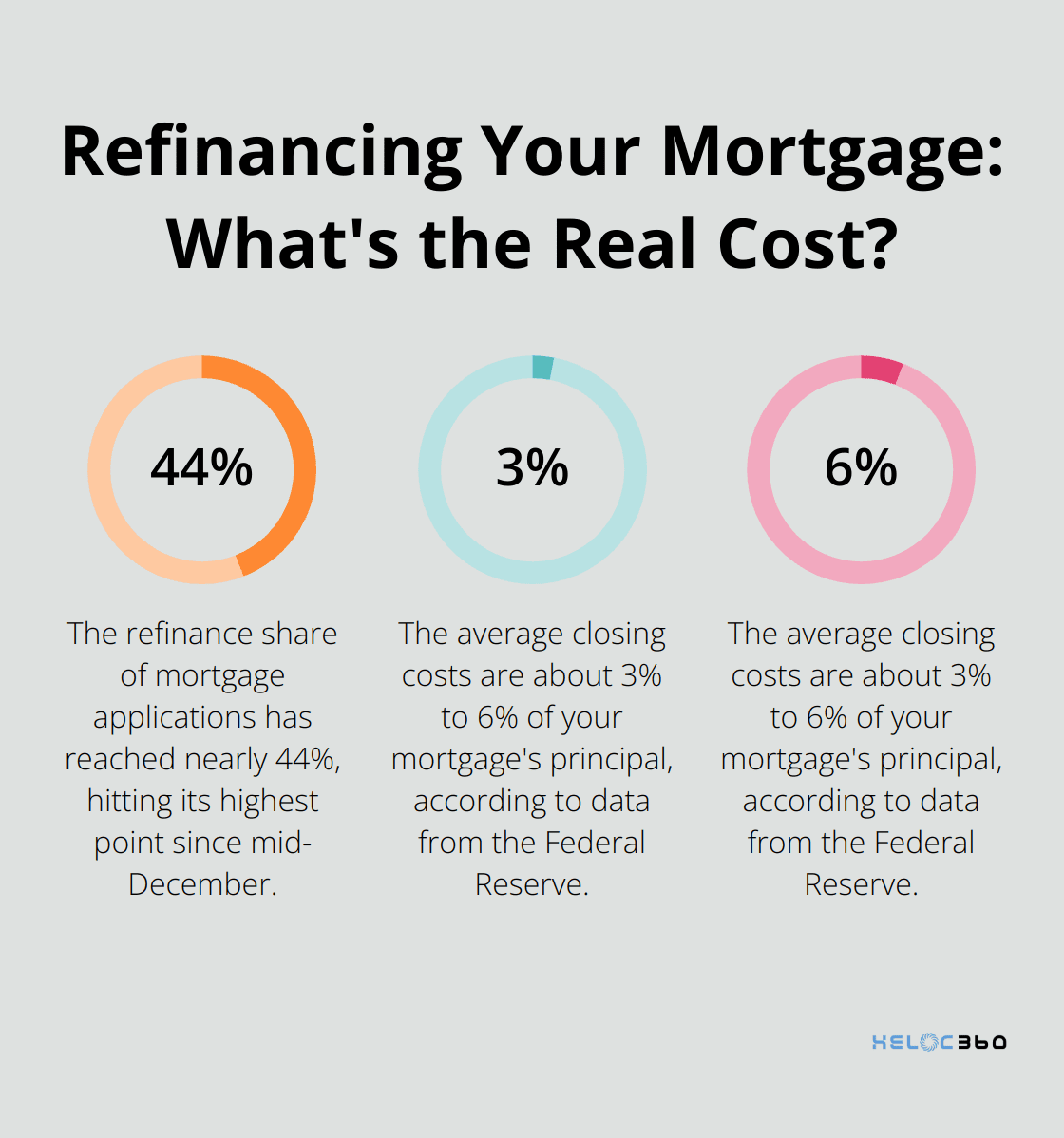
As you weigh your options between refinancing and other financial tools like HELOCs, consider how each choice aligns with your long-term financial strategy. The next section will provide a side-by-side comparison of these approaches to help you determine which option might best suit your unique situation.
HELOC vs Refinance: A Comprehensive Comparison
Monthly Payments and Long-Term Costs
HELOCs offer lower initial payments during the draw period. You typically pay interest only on the borrowed amount. However, payments can increase significantly during the repayment period when you start paying back the principal.
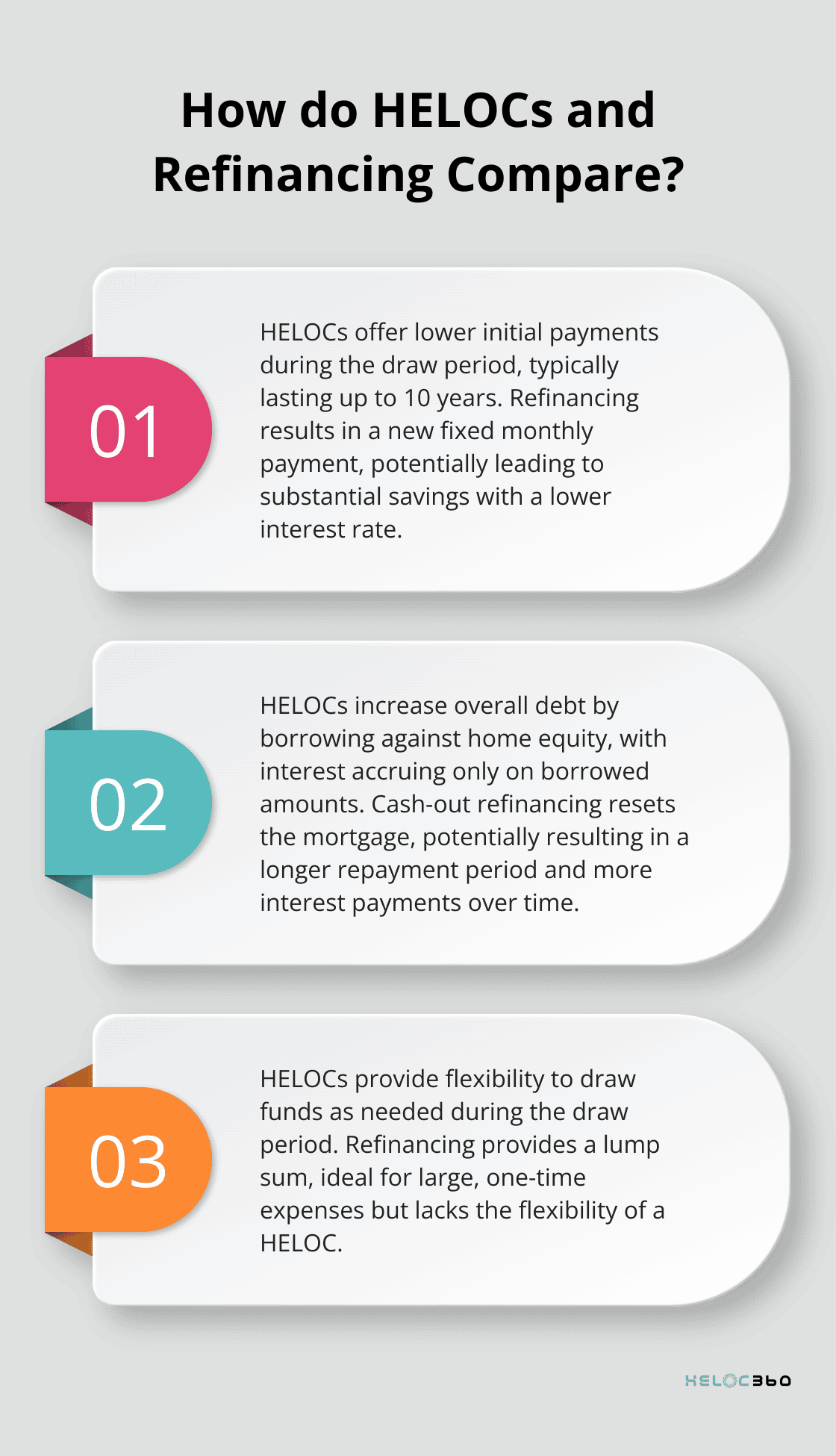
Refinancing usually results in a new fixed monthly payment. If you secure a lower interest rate, this could lead to substantial savings.
Impact on Home Equity and Debt
A HELOC increases your overall debt as you borrow against your home’s equity. You accrue interest only on the amount you borrow, not the entire credit line.
Cash-out refinancing also affects your home equity. You reset your mortgage, which could mean a longer repayment period. This might result in more interest payments over time, even if your monthly payments decrease.
Flexibility in Fund Access and Repayment
HELOCs provide unparalleled flexibility. You can draw funds as needed during the draw period, which typically lasts up to 10 years. This makes HELOCs ideal for ongoing expenses or projects with uncertain costs.
Refinancing provides a lump sum, which benefits large, one-time expenses. However, it lacks the flexibility of a HELOC. After refinancing, you can’t easily access additional funds without another refinancing process.
Tax Implications
The tax implications of HELOCs and refinancing can significantly impact your decision. Interest on HELOCs may qualify for tax deductions if you use the funds for home improvements. However, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 placed limitations on these deductions.
For refinancing, the interest on your new mortgage generally qualifies for tax deductions, subject to certain limits. If you opt for a cash-out refinance and use the funds for home improvements, that portion of the interest may also qualify for deductions.
Consult with a tax professional to understand how these options might affect your specific tax situation. The rules can change over time, so expert guidance proves invaluable.
Final Thoughts
The choice between a HELOC and refinancing will shape your financial future. HELOCs offer flexibility for ongoing projects, while refinancing can secure lower interest rates and provide lump sums. Your decision should align with your long-term goals, current interest rates, home equity, and credit score.

HELOC360 simplifies the process of leveraging your home equity. Our comprehensive solutions connect you with lenders that match your unique needs. We provide expert guidance to help you make informed decisions about using your home’s value.
The right choice in the HELOC vs refinance debate depends on your individual circumstances. You should seek expert advice to make a decision that aligns with your financial goals. HELOC360 can help you unlock the full potential of your home equity and set you on the path to success.
Our advise is based on experience in the mortgage industry and we are dedicated to helping you achieve your goal of owning a home. We may receive compensation from partner banks when you view mortgage rates listed on our website.
